Glioblastoma (GBM) Experimental Section
2024-5-23
Main Materials: Aloe-emodin (AE, 99%, Chengdu Alpha). Zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn (NO3)2·6H2O, 99.998%, Aladdin), N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS, 98%, Aladdin), N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl, 98%, Aladdin), 2-methylimidazole (C4H6N2, 98%, Aladdin), transferrin (95%, Aladdin).
from Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). And alanine aminotransferase (ALT) assay kit,creatinine (CRE) assay kit, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) assay kit, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) assay kit, γglutamyl transferase (γ-GT) assay kit were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering ResearchInstitute Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China).Synthesis of AE@ZIF-8 NPs: AE-loaded ZIF-8 NPs (AE@ZIF-8 NPs)
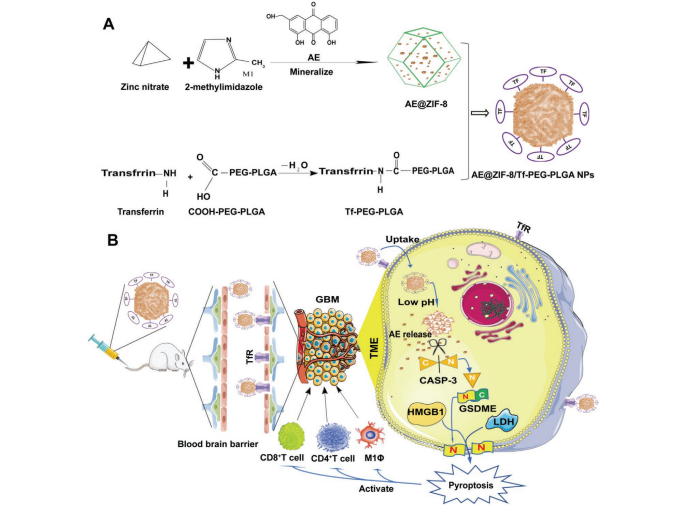
were prepared by a self-assembly method.[19,49]First, 75 mg of zinc nitrate was added to 2.5 mL of methanoland sonicated to dissolve with a 120 W ultrasonic bath for 2 min (solution A). Meanwhile, 165 mg of 2-methylimidazole and aloe-emodin (0, 2, 6, 10, 20 mg) were dissolved in5 mL of methanol and sonicated with a 120 W ultrasonic bath for 5 min (solution B). Subsequently, solution B was stirred for 5 min at 250 rpm under room temperature. Next, solution A was dropped into solution B under 250 rpm stirring condition. After that, the mixture was continue stirred in the dark at room temperature for 1 h, and then kept for another
1 h at 4 °C. Finally, the mixture was centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 10 min, washed with methanol three times to obtain AE@ZIF-8 nanoparticles, and resuspended in 5 mL methanol or normal saline (NS) containing
1% poloxamer (F127) (1% F127 NS) for further experiments.Preparation of Tf-PEG-PLGA: Tf was conjugated to PEG-PLGA by a two-step EDC/NHS coupling method.[50]
With the catalysis of EDC/NHS, the COOH of COOH-PEG-PLGA interacts with NH2 from
Tf to generate amide bonds, thereby obtaining Tf-modified PEG-PLGA (Tf-PEG-PLGA) (Scheme 1A). Briefly, 10 mg COOH-PEG-PLGA was dissolved in 4.5 mL methanol in a 120 W ultrasonic bath for 5 min, then
250 µL of EDC·HCl (1 mg mL−1) and 250 µL of NHS (1 mg mL−1) were added and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 4 h at 250 rpm. Then, 200 µL of transferrin aqueous solution (1 mg mL−1) was added
dropwise, stirred in the dark for 2 h, and incubated for overnight at 4 °C.Preparation of AE-NPs: The above AE@ZIF-8 NPs methanol solution was mixed with Tf-PEG-PLGA methanol solution in volume ratios of
5:5, 6:4, 7:3, 8:2, and 9:1 at room temperature with magnetic stirring at 250 rpm for 4 h in the dark. The samples were centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 10 min, and the precipitate was taken to obtain the final AE-NPs
product, which was washed twice with methanol. Then, the NPs were resuspended in 75% ethanol, soaked for 30 min to remove bacteria, and washed twice with 1% F127 NS.Characterizations of ZIF-8 NPs, AE@ZIF-8 NPs, and AE-NPs: Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to detect the size of nanoparticles. For detection nanoparticle size and zeta potential, the NPs were distributed in methanol, 1% F127NS, and 1% F127NS+10% FBS, respectively, and analyzed by a Malvern laser particle size analyzer (DTS1070, Malvern, UK). The stability of nanoparticles was evaluated by hydrodynamic particle size at 0, 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. The structure and morphology of blank ZIF-8 NPs, AE@ZIF-8 NPs, and AE-NPs were observed by TEM (HITACHI, Japan) with an accelerating voltage of 80 kV. TEM samples were tweezers
held on carbon-coated copper grids (200 mesh; Ted Pella, Inc., USA), immersed in a particle solution, removed, and air-dried prior to imaging. The size from TEM was analyzed with ImageJ software. Each picture
was marked with 100 nanoparticles, three pictures were recorded, and the detection results were imported to Origin 2021 software to obtain the size. Furthermore, the successful encapsulation of AE and ICG
into Tf-PLGA-PEG coated ZIF-8 NPs was detected through remarkable absorption at 255 and 780 nm by UV–vis absorption spectroscopy (Puxi General Instrument Co., Ltd. China). The coating of Tf-PEG-PLGA on
ZIF-8 NPs was confirmed by FTIR spectra and TEM images.Drug Loading Degree and Efficiency Detection: The content of AE was detected by UV–vis absorption at 255 nm. A 200 µL sample was dropped into a cuvette containing 2.8 mL methanol solution with a pH of 1.5. According to the standard curve, the content of AE in the sample was calculated. AE loading degree (LD, %) = amount of encapsulated AE/weight of nanoparticles; AE encapsulation rate (%) = amount of encapsulated AE/total input amount of AE. the connection efficiency of
transferrin was calculated by a BCA kit, Tf loading efficiency (LE, %) =weight of transferrin in nanoparticles/total input amount of transferrin.In Vitro Release and pH-Responsive Analysis: AE-NPs were dispersed into 1.0 mL of 1% F127 NS (pH = 7.4; pH = 5.5) and shaken at 37 °C gently in dark. The solution was first centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 10 min, and then 900 µL of supernatant was withdrawn and analyzed by a UV spectrophotometer at 255 nm at indicated time points. Then, 900 µL of fresh medium was added and sonicated until dispersed well. Calculate cumulative release rates at selected time intervals. The alternative sample disposal method is as above. At selected time intervals, the appearance of AE-NPs from different pH values was observed by TEM,
and size was test by Malvern laser particle size analyzer.Cells and Animals: U87MG, DBTRG, U251, HeLa, HepG2, A549, HMO6, BV2 cells were purchased from ATCC (American TypeCulture Collection) and stored in the laboratory and cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS, 1% penicillin–streptomycin solution, 2 mm l-glutamine, and maintained at 37 °C with 5% CO2 humidity. GL261-Luc was purchased from Shanghai Yansheng Industrial Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China), and used as the transplanted tumor model. GL261-Luc cells were stored as recommended by ATCC, cultured and cryopreserved according to the manufacturer’s protocol. C57BL/6J mice were purchased from Laboratory Animal Center of Hubei University of Medicine (Hubei, China) and bred according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health.
The experimental protocol of this study was reviewed and approved by the Laboratory Animal Welfare Ethics Review Committee of Hubei University of Medicine (Hubei University of Medicine Animal (welfare) No. 2022-Experiment 015).
上海研生实业有限公司 版权所有
直接在手机上打开